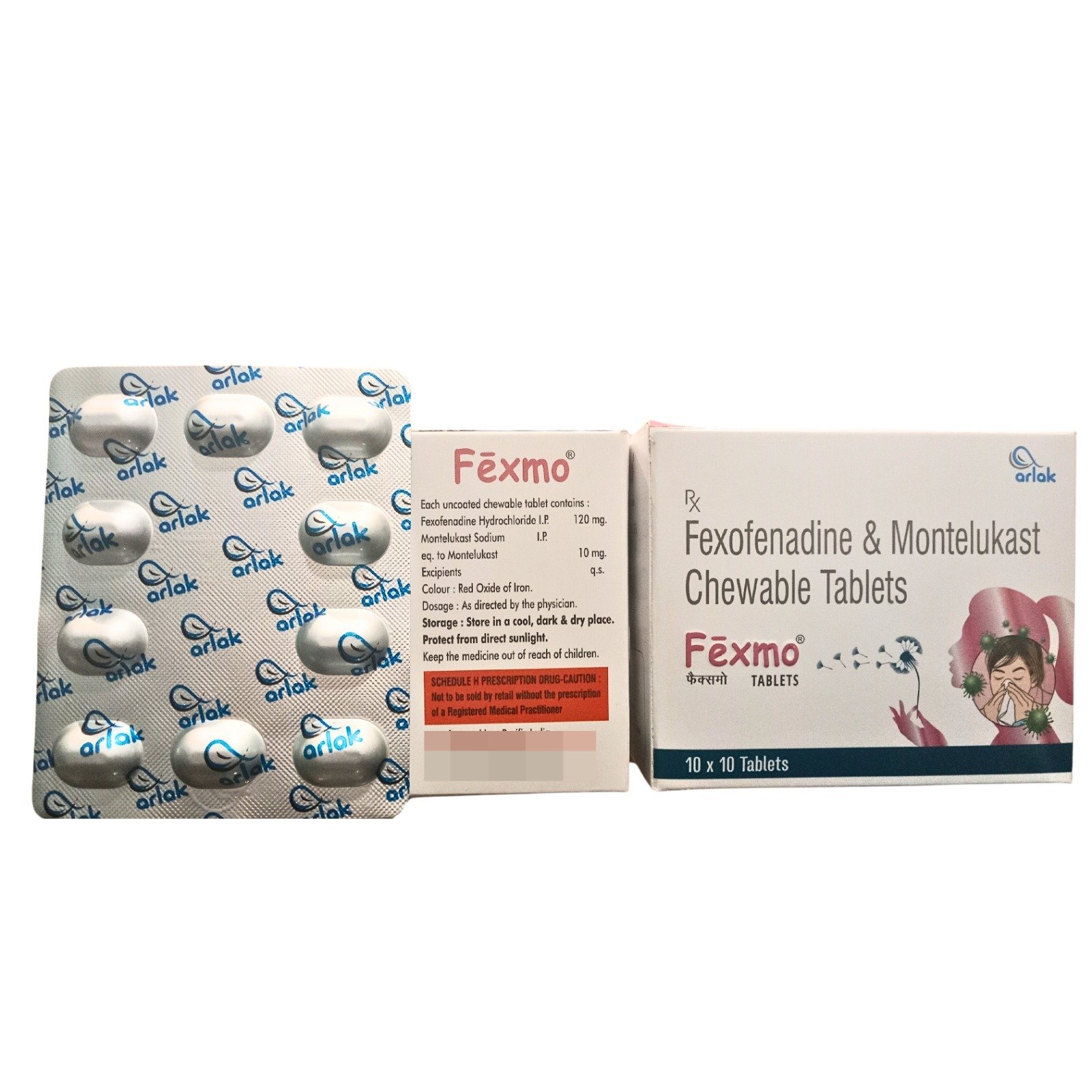
Description
Amoxicillin is a semisynthetic antibiotic with a broad spectrum of bactericidal activity against many gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. Amoxicillin is, however, susceptible to degradation by Beta-lactamases, and therefore, the spectrum of activity does not include organisms which produce these enzymes.
Clavulanic acid is a Beta-lactam, structurally related to the penicillins, which possesses the ability to inactivate a wide range of Beta-lactamase enzymes commonly found in microorganisms resistant to penicillins and cephalosporins. In particular, it has good activity against the clinically important plasmid-mediated Beta-lactamases frequently responsible for transferred drug resistance.
PHARMACOLOGY
PHARMACOKINETICS: –
ABSORPTION: – Amoxicillin is stable in the presence of gastric acid, oral absorption is better, presence of food does not interrupt with its absorption.
DISTRIBUTION: – Diffusion of the drug takes place into most body tissues and fluids, but it does not crosses the blood brain barrier and the spinal fluid. It crosses the placenta; small amounts are distributed into breast milk.
INDICATIONS: –
- Acute bacterial sinusitis (adequately diagnosed)
- Cystitis
- Pyelonephritis
- Cellulitis
- Animal bites
- Severe dental abscess with spreading cellulitis.